Thyroid Balance: Hypo vs. Hyper
Hypothyroidism vs. Hyperthyroidism: Understanding the Balancing Act of Your Thyroid
Welcome to our exploration of the fascinating world of thyroid health! If you’ve ever felt like your energy levels are on a rollercoaster ride or noticed changes in your weight, mood, or overall health, you might be wondering about the role your thyroid plays. Today, we’ll dive into the differences between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, making it easy to understand what each condition means and how they affect your body.
What is the Thyroid?
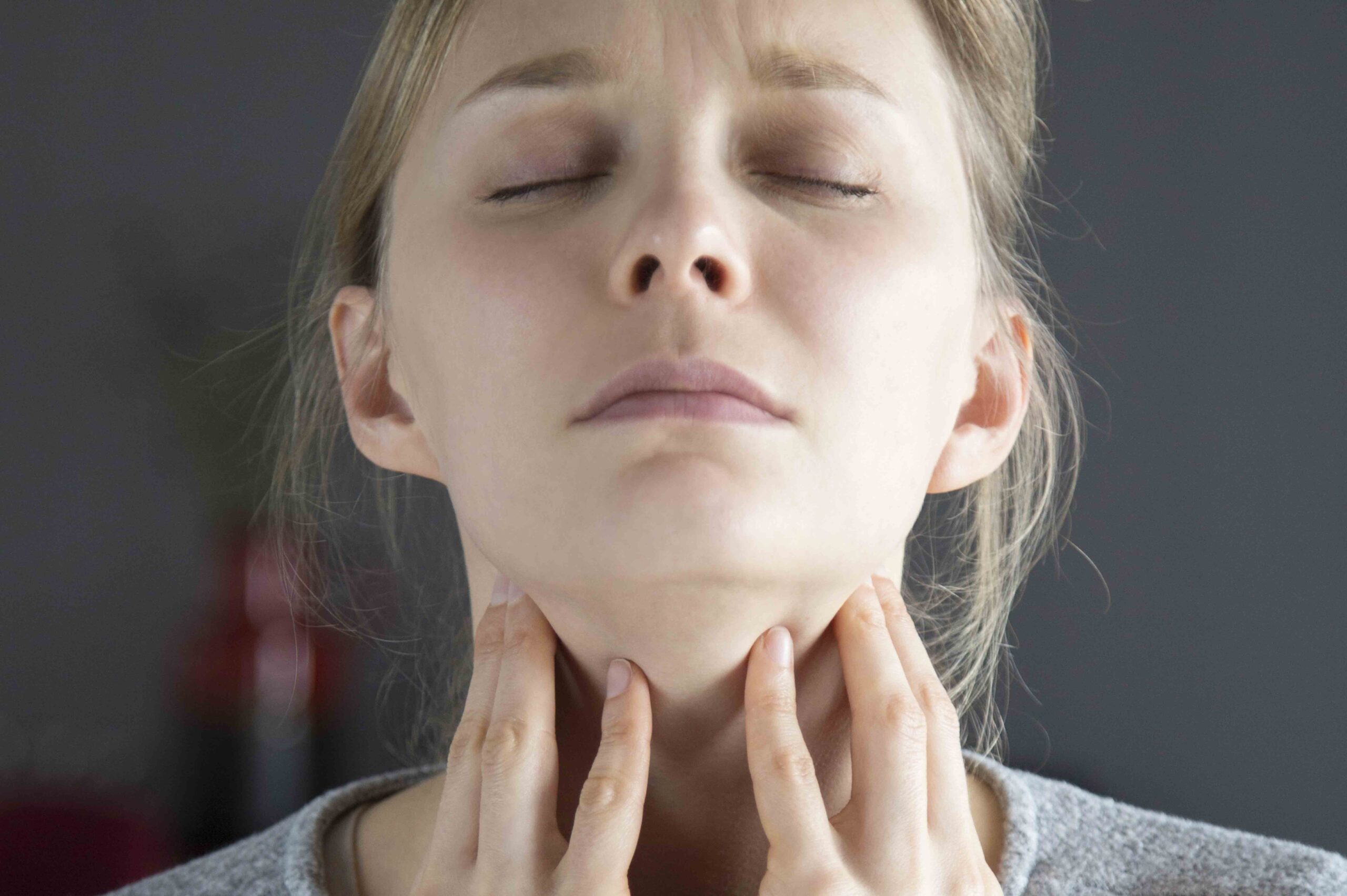
First, let’s get acquainted with the thyroid gland. This butterfly-shaped gland is located at the base of your neck and plays a crucial role in regulating your metabolism, energy production, and overall hormonal balance. It produces hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) that help control how your body uses energy.
Hypothyroidism: The Underachiever
Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid gland is underactive, meaning it doesn’t produce enough hormones. This condition can lead to a slowdown in your metabolism, resulting in various symptoms, including:
– Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired even after a good night’s sleep.
– Weight Gain: Gaining weight without changing your diet or exercise routine.
– Cold Sensitivity: Feeling cold when others are comfortable.
– Dry Skin and Hair: Notice your skin becoming dry or your hair thinning.
– Mood Changes: Experiencing depression or sluggishness.
In the United States, hypothyroidism is commonly caused by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. Other causes include certain medications, radiation therapy, and iodine deficiency.
Hyperthyroidism: The Overachiever
On the flip side, hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive and produces excess hormones. This condition speeds up your metabolism, leading to symptoms such as:
– Weight Loss: Losing weight unexpectedly or despite eating normally.
– Increased Heart Rate: Feeling your heart racing or pounding
– Nervousness and Anxiety: Experiencing increased anxiety or irritability.
– Heat Intolerance: Finding it difficult to tolerate heat or sweating excessively?
– Sleep Difficulties: Struggling to fall asleep or stay asleep?
Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism and is also an autoimmune condition. Other causes may include toxic nodular goiter or excessive iodine intake.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disorders
If you suspect you have a thyroid disorder, the first step is to consult with a doctor. They will likely conduct a physical examination and order blood tests to measure hormone levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. A high TSH level usually indicates hypothyroidism, while low TSH levels suggest hyperthyroidism.
Treatment Options
The treatment for hypothyroidism typically involves hormone replacement therapy, where synthetic thyroid hormones are prescribed to restore normal hormone levels. Conversely, hyperthyroidism may be treated with antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine, or even surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism is essential for recognizing symptoms and seeking timely treatment. Remember, your thyroid plays a significant role in your overall health and well-being, and keeping it balanced is key to feeling your best. If you notice any symptoms or have concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor!